Tutong District
Tutong District
| |
|---|---|
|
Clockwise from top left: Tutong Town, Tutong River, Mukim Keriam, Pantai Seri Kenangan | |
 | |
| Country | Brunei |
| Administrative centre | Tutong Town |
| Mukims | 8 (see Mukims) |
| Government | |
| • Type | Municipality |
| • Body | Tutong District Office |
| • DO | Mohammad Sofian Basri (Acting) |
| Area | |
| • Total | 1,166 km2 (450 sq mi) |
| • Rank | 3rd in Brunei |
| Highest elevation | 529 m (1,736 ft) |
| Population (2021)[3] | |
| • Total | 47,210 |
| • Rank | 3rd in Brunei |
| • Density | 40/km2 (100/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC+8 (BNT) |
| Postcode | T[4] |
| Area code | 4[4] |
| Website | www.tutong.gov.bn |
Tutong District (Malay: Daerah Tutong; Jawi: دائيره توتوڠ) or simply known as Tutong (tu-tong),[5] is the third largest and populated district in Brunei.[6] It has an area of 1,166 square kilometres (450 sq mi) and the population of 47,210 as of 2021. The district is also home to its administrative centre is Tutong Town (Pekan Tutong), as well as the Tutong River and Tasek Merimbun, the country's second longest river and the only ASEAN Heritage Parks in Brunei respectively.[5]
Geography
[edit]The district borders the South China Sea to the north, Brunei–Muara District to the northeast, Sarawak to the east and south, and Belait District to the west. Covering 1,166 square kilometres (450 sq mi), it is the third-largest district in Brunei.[7] The 137 kilometre Tutong River,[8] the district's primary river, flows from the interior in the south to the South China Sea.[7] Bukit Bedawan, the district's highest point, stands at 529 meters.[9] The district also hosts Tasek Merimbun, Brunei's largest natural lake, designated as an ASEAN Heritage Park since 29 November 1984.[10]
Compared to Temburong District, which is isolated from Brunei proper, Tutong is in a more beneficial position due to its extremely strategic placement between the Brunei–Muara and Belait districts. This is due to the fact that, despite having less economic potential than Temburong, the Tutong District benefits from a better location in terms of development, as all major roads and highways pass through it and connect the state's administrative center, the Belait District, with Brunei's economic centre, the Brunei–Muara District.[11]
History
[edit]Tutong was formerly a part of the Melanau administration in the 14th century before joining the Bruneian Empire in the 15th.[12]
Early in 1901, Dato Di Gadong organised an uprising in Tutong, purportedly with the backing of Rajah of Sarawak, Sir Charles Brooke, who wanted to use Brunei's instability as a pretext for annexing the area. Brooke's proposal was thwarted when the British authorities cautioned him not to intervene. While most rebels received amnesty from the Bruneian authorities, Dato Di Gadong and Dato Kalam of Limau Manis were left out and fled to Limbang, where they were found guilty of stealing carabao. When Dato Di Gadong returned to Tutong illegally in 1902, Sultan Muhammad Jamalul Alam II ordered his death. Dato Di Gadong was also suspected of many killings.[13]
Prior to the introduction of the British Residency in Brunei in 1906, Tutong was a kuripan (belonging to state officials), a type of land ownership in Brunei's traditional government. It was the non-hereditary land of Pengiran Di-Gadong, one of the four traditional Wazirs to the Sultan.[14] Healthcare in the district began with the establishment of a medical clinic in 1932 in Bukit Bendera area near the district town Pekan Tutong.[15] Before the Tutong Bridge was built in 1959, Brunei Town (present day Bandar Seri Begawan) and Brunei's southern districts could only be reached by ferrying between Danau and Kuala Tutong.[16]
In 1967, the government moved quickly to provide areas that the local populace needed and found convenient. A modern B$500,000 structure was also constructed in lieu of the government building. A community centre, playground, police and fire stations, a carpentry school, an English primary school, a telecom facility, and guest residences for the village chief and district officer are among the other structures that were constructed. In addition, wells, bridges, and paved roads have been constructed to raise the level of living. The district have seen a rapid rise in population by nearly 15,000 in that same year.[17]
Administration
[edit]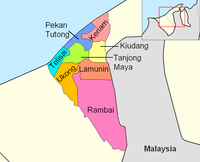
The procedures for the board's business conduct are outlined in the Tutong Municipal Board (Standing Orders) By-Laws, 2014. Meeting procedures, such as notification requirements, quorum requirements, and the responsibilities of the chairman and secretary, are outlined in the bylaws. Members must adhere to certain voting and speaking procedures, and meetings must begin with a prayer. The chairman is in charge of the meeting, and every motion needs to be submitted in writing and seconded before it can be discussed. These bylaws guarantee the Municipal Board's organised and orderly governance.[18]
The district is administered by the Tutong District Office (Jabatan Daerah Tutong), a government department under the Ministry of Home Affairs. The district is subdivided into 8 mukims, namely:[6][19]
| Mukim | Population (2021)[3] | Penghulu (2024)[20] |
|---|---|---|
| Keriam | 8,589 | Haji Joharry bin Haji Abdul Karim |
| Kiudang | 5,063 | Mohd Jaafar bin Haji Tinggal |
| Lamunin | 3,641 | |
| Pekan Tutong | 9,883 | Salim bin Haji Othman |
| Rambai | 980 | Mohammad Dahalan bin Kaslan |
| Tanjong Maya | 3,772 | Mohammad Azaman Shah bin Haji Sahari |
| Telisai | 13,253 | Haji Haslan bin Haji Shahbuddin |
| Ukong | 2,029 | Haji Mohamad Danial @ Tekpin bin Ya’akub |
According to the Constitution, the district is to be represented in the Legislative Council, the state legislature, by up to 7 members.[21] As of 2023, two members have been appointed to represent the district in the legislature.[22]
Demographics
[edit]The main ethnic groups in the district consist of Tutong, Dusun, Kedayan, Iban and Chinese.[23] Since much of Tutong's interior is still covered in dense forest, where some of the non-Malay indigenous people live, the majority of the population resides along the shore.[6] In 2020, the district's population was estimated to have increased to 51,500.[24]
Transportation
[edit]Road
[edit]
Additional road infrastructure improvement projects, including those in Tutong District, will be implemented through the National Development Plan (RKN) 2007–2012. These projects include the first phase of widening Jalan Lamunin (earthworks), the construction of small roads along Kampong Batang Mitus, Kampong Kebia, and Penapar Bridge to Lubok Pulau, and the third phase of replacing the current wooden bridges.[25] The Muara–Tutong Highway is the main route running across Tutong, which connects to the Brunei–Muara and Belait districts.[26][27]
Water
[edit]Due to a shallow, sandbar that shifts periodically near the river mouth, Tutong Town, which is located on the northern bank of the Tutong River approximately 8 miles upstream, has few shipping options. The settlement has a 20-foot wooden pier that is mostly used by government patrol boats and indigenous vessels. Kuala Tutong on the north bank is connected to Danau on the south bank by a government-run car ferry service. The M.A. "Pemancha," a bigger all-steel vessel that was introduced in May, has boosted traffic and enhanced the efficiency of this ferry service, which is essential for connecting the two sides of the state. In addition, Tutong issued licenses to eighteen fishing vessels in 1957.[28]
Tenders have been called for the design and construction of two large bridge sites, one over the Tutong River near Tutong and another over the Telamba River near Telisai, which will replace the Kuala Tutong Ferry service. A 12 miles (19 km) route has been surveyed and found favorable for road construction earlier in 1953.[29] On 25 December 1958, Tutong–Danau ferries came to a stop, signaling the end of an era.[30] The Tutong Bridge was opened in 1959,[16] this allowed continuous vehicle movement from Bandar Seri Begawan through Tutong was made feasible by the bridge over the river.[31]
Economy
[edit]The district's primary industries include forestry, fishing, and the production of rice and rubber, with shifting agriculture being practiced by the non-Malay indigenous population.[6]
Agriculture
[edit]The agriculture sector has received a lot of attention in the effort to diversify the economy since it has a lot of room to develop. The Tutong District has set aside 3,804.15 hectares for agricultural development zones, which include Sungai Paku, Kupang, Maraburong, and several other localities. With 129.41 hectares of land set aside for rice production in 2009—a yield of 190.37 metric tons involving 425 farmers—Tutong is likewise acknowledged as a major producer of paddy. Eight of the 24 sawmills that are now in operation in Brunei are located in Tutong.[32]
In 2022, the Tutong District was allocated a total of 1,913.81 hectares (4,729.1 acres) for agricultural development. Of this, 573.53 hectares were designated for farming by local farmers, while 305.45 hectares were utilized for stations and other purposes. This allocation is part of a broader national initiative that also includes the Brunei–Muara, Belait, and Temburong districts, contributing to a total of 9,666.69 hectares gazetted for agricultural development across the country.[33]
The Tutong District's Agricultural Development Areas (KKP) span 1,913.81 hectares in total, of which 305.45 hectares are set aside for stations and other purposes and 573.53 hectares are granted to farmers. Important regions are KKP Kupang, which is devoted to fruits, vegetables, and integrated crops, and KKP Batang Mitus Buah and Halaman, which concentrate on fruits and other miscellaneous crops. Other noteworthy regions include KKP Sinaut for integrated crops and floriculture, and KKP Maraburong for fruits and vegetables. Furthermore, a number of stations are set aside for certain agricultural uses, such processing, chicken, and hatcheries.[34]
Agrifood
[edit]In Tutong District, livestock production in 2022 included 77 kilograms of deer and various non-ruminant livestock such as 17,164 kilograms of village fowls, 119 kilograms of Muscovy ducks, 80 kilograms of ducks, and 858 kilograms of quail. Egg production comprised 598 kilograms of village fowl eggs, 0 kilograms of goose eggs, 34 kilograms of Muscovy duck eggs, 287 kilograms of duck eggs, and 284 kilograms of quail eggs. The total livestock and egg production in Tutong amounted to 19,499 kilograms.[35]
Fisheries
[edit]The majority of Tutong's fishermen work part-time jobs and mostly fish the Tutong Estuary and the northwest region of Tutong. They use a range of inshore fishing gear, including as pots or traps, tidal weirs, ring nets, trammel nets, gill nets with greater mesh sizes, several kinds of seines, and corral nets. Hand lines, cast nets, lift nets, drift gill nets, and intertidal funnel barrier nets are among the other equipment employed. These are essential fishing instruments in Tutong's estuary habitat.[36] Golden Corporation has its organic blue shrimp production and product range by acquiring 200 hectares (490 acres) of land in Kampong Penyatang.[37]
Development
[edit]
The Pengiran Muda Mahkota Pengiran Muda Haji Al-Muhtadee Billah Hospital, which has 138 beds and medical equipment, is the primary healthcare institution since late 1972.[38][39] It provides a wide range of services, including as emergency services, outpatient treatment, and specialty clinics. In addition, the district has four health centers, many mobile clinics, and a flying-doctor service for rural communities. The district's healthcare services will be enhanced by new projects, one of which is a dialysis facility, as part of the RKN 2007–2012.[40] The Tutong District hosts the National Isolation Centre, a key facility for isolating and treating communicable diseases, including COVID-19, with an initial capacity of 136 beds and a 2020 extension adding 160 more beds, funded at a total cost of B$19.47 million.[41][42]

The National Housing Programme, initiated in the 1950s, introduced various schemes such as the Infill Scheme (IS), Temporary Occupation-of-Land License (TOL), and the Landless Indigenous Citizens' Housing Scheme (STKRJ) to address housing needs. In Tutong District, similar housing initiatives were implemented, including the National Housing Scheme (RPN) Bukit Beruang,[43] STRKJ Kampong Lugu,[44] and STKRJ Kampong Telisai.[45]
In the Tutong District, government schools are primarily managed by the Ministry of Education and include 23 kindergartens and primary schools, 5 secondary schools, and one sixth form college,[46] all part of Cluster 5 of the Ministry's school administrative district.[47] Notable secondary schools are Muda Hashim, Raja Isteri Pengiran Anak Saleha, Sayyidina 'Othman, Sufri Bolkiah, and Tanjong Maya, offering education leading to Brunei-Cambridge GCE O Levels.[48] The district's sole sixth form institution is the Tutong Sixth Form Centre, which provides education leading to GCE A Levels.[49][46] Additionally, Ma'had Islam Brunei, administered by the Ministry of Religious Affairs, is dedicated to Arabic-medium Islamic education and offers levels leading to the Sijil Pelajaran Ugama Brunei (Bruneian Certificate of Religious Education).[50] In order to build UNISSA Sinaut Campus, the organisation obtained the Sinaut Agricultural Training Centre.[51][52]
The water sector's RKN 2007–2012 has a strong emphasis on growing water resources, making sure they are available during dry seasons, boosting water treatment capacity to meet demand plus 20%, and lowering unaccounted water while raising quality standards. This was accomplished by building two dams in Belait River, Ulu Tutong and Benutan, with a combined storage capacity of 89,000,000 cubic metres (3.1×109 cu ft). In addition, the 140-acre Bukit Panggal Power Station was constructed at a cost of more than B$161 million to accommodate the rising demand for energy. Future upgrades include the construction of a second phase combined cycle power station in Tutong District.[53]
Tourism
[edit]Commerce
[edit]
Shophouses in Tutong Town may be found on one side, while the wide Tutong River with its far bank covered in palm trees is on the other. There are a few eateries in Tutong, including the Chinese Ho Yuen at number 12 and the Haji K-K-Koya at Jalan Enche Awang 14.[54] Travelers may have a more secure base of operations and an easier time seeing the area by staying in Tutong's hotels and homestays. The most traditional option for lodging is a hotel. In the Tutong area, The Lanes Hotel,[55] Telamba Homestay,[56] and Eco Ponies Garden are a few suggested possibilities.[57]
Landmarks
[edit]
Tutong Market, a wet market managed by the Tutong Municipal Board,[58] is located outside the municipal area in Serambangun.[59] The oldest mosque in the district, Hassanal Bolkiah Mosque, serves the Muslim residents of Tutong as well as nearby villages like Panchor Dulit, Panchor Papan, and Serambangun.[60] Notable landmarks include the Mercu Tanda Kenangan (The Keris Monument) and Warisan Emas, which commemorate Sultan Hassanal Bolkiah's 58th and 60th birthdays, respectively.[61] Additionally, Istana Pantai, a palace built by Omar Ali Saifuddien III in the 1950s, stands as a historical site in the district.[62]
Recreation
[edit]Pantai Seri Kenangan, a well-liked beach with picnic areas, fishing locations, and facilities like playgrounds and eateries, is one of Tutong's array of attractions.[59] Another great beach for picnics and shell collection is Pantai Persiaran Pengkalan Pinang Penanjong. Sungai Basong Recreational Park, which is close to Tutong Town, has a variety of amenities, ethnic tiny homes, and beautiful paths. Unique tree species are on display at Tumpuan Telisai Recreational Park, which also provides a range of recreational opportunities. For scientific purposes, Tasek Merimbun Heritage Park, an ASEAN National Heritage Site since 1984, protects its fauna and plants.[59]
The district boasts several points of interest, including Pantai Pengasing in Kampong Sengkarai, the Tutong Riverfront in Pekan Tutong, and Gerai Selera Tutong. Visitors can explore natural sites like Bukit Ambok in Kampong Suran, Pulau Tanjong Maya, and the scenic Wasai Bedanu in Kampong Kiudang. Other attractions include Bukit Kukub in Kampong Bukit Udal, Rumah Warisan in Kampong Kupang, and Pantai Danau. The area also features various local markets such as Tamu Kampung Long Mayan and Gerai Mukim Telisai, as well as cultural spots like Kampong Kebubok Long House.[63] Alai Gayoh Anak Pulau is a traditional Dusun wooden house turned into a serene retreat overlooking Bukit Udal's lush greenery. Eco Ponies Garden offers a peaceful homestay experience with sustainable farming and traditional kampong cuisine in Lamunin's rainforests, while Wasai Bedanu is a hidden waterfall in the dense Tutong rainforest, perfect for a refreshing swim amidst nature's beauty.[59] Facilities for playing football, athletics, swimming, tennis, badminton, and basketball are available at Tutong Sports Complex.[64]
References
[edit]Citations
[edit]- ^ "Ketua_ketua Jabatan dan Timbalan/Penolong Ketua Jabatan". Ministry of Home Affairs (in Malay). Retrieved 2 September 2024.
- ^ Haji Julaini & Haji Idris 2012, p. 8.
- ^ a b "Annex B" (PDF). DEPS.MoFE.gov.bn. Department of Economic Planning and Statistics, Ministry of Finance and Economy. October 2021. Retrieved 23 January 2024.
- ^ a b "Postcode". Ministry of Transport and Infocommunications. Retrieved 2 September 2024.
- ^ a b Cohen 2008, p. 3981.
- ^ a b c d Sidhu 2009, p. 50-51.
- ^ a b Haji Julaini & Haji Idris 2012, p. 7.
- ^ Bac-Bronowicz, Joanna; Becek, Kazimierz (2021). "Environmentally based perception of space". ResearchGate. Retrieved 4 August 2021.
- ^ "BRUNEI" (PDF). www.diplomatie.gouv.fr (in French).
- ^ Fadley Faisal (31 December 2020). "Tasek Merimbun Heritage Park closed for maintenance". Borneo Bulletin Online. Retrieved 4 August 2021.
- ^ Sidhu 2009, p. 236.
- ^ Mohd Yunos, Rozan (2013). SEMINAR UNITED NATIONS GROUP OF EXPERTS ON GEOGRAPHICAL NAMES ASIA, SOUTHEAST DIVISION (PDF). p. 22.
- ^ Sidhu 2009, p. 71.
- ^ Horton, A. V. M. (1987). "The Disturbances in the Tutong and Belait Districts of Brunei (1899-1901)". Journal of Southeast Asian Studies. 18 (1). Cambridge University Press on behalf of National University of Singapore: 93–107. doi:10.1017/S0022463400001272. JSTOR 20070944. S2CID 163087527. Retrieved 3 August 2021.
- ^ Pusat Sejarah Brunei 2002, p. 138.
- ^ a b Explore Brunei: A Visitor's Guide. Publications Unit, Royal Brunei Airlines. 2000. p. 38.
- ^ "Pembangunan Daerah Tutong Di-Pesatkan" (PDF). Pelita Brunei. 5 April 1967. pp. 4–5.
- ^ "MUNICIPAL BOARDS ACT (CHAPTER 57) TUTONG MUNICIPAL BOARD (STANDING ORDERS) BY-LAWS, 2014" (PDF). Attorney General's Chambers. 10 February 2014. Retrieved 3 September 2024.
- ^ Haji Julaini & Haji Idris 2012, p. 8-9.
- ^ BUKU DIREKTORI TELEFON PENGHULU-PENGHULU MUKIM DAN KETUA-KETUA KAMPUNG NEGARA BRUNEI DARUSSALAM (PDF) (in Malay). Vol. 4. Brunei: Bahagian Perancangan Daerah, Ministry of Home Affairs. April 2024. p. 25.
- ^ "CONSTITUTIONAL DOCUMENTS" (PDF). www.agc.gov.bn. p. 179. Retrieved 27 October 2021.
- ^ "New Legislative Council appointed". Borneo Bulletin Online. 20 January 2023. Retrieved 14 November 2023.
- ^ "Jabatan Daerah Tutong, Kementerian Hal Ehwal Dalam Negeri - Profail Tutong". tutong.gov.bn (in Malay). Retrieved 29 September 2017.
- ^ "Department of Economic Planning and Development - Population". www.depd.gov.bn. Retrieved 19 October 2017.
- ^ Haji Julaini & Haji Idris 2012, p. 19.
- ^ Countries and Territories of the World. Vol. 1. PediaPress. p. 398.
- ^ The Far East and Australasia 2003. Psychology Press. 2002. p. 225. ISBN 978-1-85743-133-9.
- ^ Great Britain Colonial Office (1957). Brunei. H.M. Stationery Office. pp. 152–153.
- ^ Brunei (1953). Annual Report. H.M. Stationery Office. p. 183.
- ^ Brunei (1960). Annual Report on the Social and Economic Progress of the People of Brunei. Printed at the Brunei Press. p. 168.
- ^ Khoo, Soo Hock (1976). Brunei in Transition: Aspects of Its Human Geography in the Sixties. Department of Geography, University of Malaya. p. 72.
- ^ Haji Julaini & Haji Idris 2012, p. 22-24.
- ^ Department of Agriculture and Agrifood 2022, p. 5.
- ^ Department of Agriculture and Agrifood 2022, p. 9-10.
- ^ Department of Agriculture and Agrifood 2022, p. 43.
- ^ Silvestre 1992, p. 94.
- ^ "Seafood firm to boost blue shrimp output, product range". GON. 15 January 2015. Retrieved 4 September 2024.
- ^ Pusat Sejarah Brunei 2002, p. 139.
- ^ "Ministry of Health - hpmmpmhamb". Ministry of Health. Retrieved 15 June 2022.
- ^ Haji Julaini & Haji Idris 2012, p. 20-21.
- ^ Rasidah Hj Abu Bakar (24 April 2020). "New isolation centre building set to more than double number of beds". The Scoop. Retrieved 25 September 2021.
- ^ Rohani Haji Abdul Hamid; Aryentty Haji Ariffin (13 November 2012). "DPMM berangkat rasmikan Pusat Pengasingan Kebangsaan" (PDF). Pelita Brunei (in Malay) (published 14 November 2012). Jabatan Penerangan. pp. 12–13. Retrieved 25 September 2021.
- ^ "HM presents keys to 601 new homeowners, tours Tutong - The Scoop". The Scoop. 21 February 2018. Retrieved 18 April 2018.
- ^ Haji Ismail, Hajah Rosidah (4 July 2020). "Tasik Lugu jadi tarikan pengunjung". Pelita Brunei (in Malay). Retrieved 1 September 2024.
- ^ Haji Julaini & Haji Idris 2012, p. 22.
- ^ a b "Sixth Form Colleges". Ministry of Education, Brunei Darussalam. Retrieved 4 September 2024.
- ^ "Government Education Institutions". Ministry of Education, Brunei Darussalam. Retrieved 4 September 2024.
- ^ "Secondary Education". Ministry of Education, Brunei Darussalam. Retrieved 10 September 2016.
- ^ "Post Secondary Education". Ministry of Education, Brunei Darussalam. Retrieved 10 September 2016.
- ^ "Pengumuman". Ministry of Religious Affairs (in Malay). 22 May 2024. Retrieved 4 September 2024.
- ^ Mohamad, Lyna (16 September 2023). "Educators, officers gain agricultural insight during visit". Borneo Bulletin Online. Archived from the original on 6 August 2024. Retrieved 6 August 2024.
- ^ Ak Zaki Kasharan (8 July 2022). "Penyerahan kampus pertanian UNISSA di Sinaut". Media Permata Online (in Malay). Archived from the original on 8 July 2022. Retrieved 6 August 2024.
- ^ Haji Julaini & Haji Idris 2012, p. 17-18.
- ^ Ledesma, Charles de; Lewis, Mark; Savage, Pauline; Guides (Firm), Rough (2003). Malaysia, Singapore and Brunei. Rough Guides. p. 598. ISBN 978-1-84353-094-7.
- ^ "The Lanes Hotel Brunei Darussalam | Tutong's Finest Hotel". The Lanes Hotel. Retrieved 4 September 2024.
- ^ "Telamba Homestay". Radio Television Brunei. 13 October 2017. Retrieved 4 September 2024.
- ^ "Eco Ponies Garden". Brunei Tourism Official Site. 13 January 2023. Retrieved 4 September 2024.
- ^ "Bandaran Tutong, Kementerian Hal Ehwal Dalam Negeri - Aset-Aset Jabatan". bandaran-tutong.gov.bn. Retrieved 30 August 2017.
- ^ a b c d "Tutong". Brunei Tourism Official Site. 29 July 2019. Retrieved 4 September 2024.
- ^ "SenaraiMasjid - Masjid Hassanal Bolkiah, Pekan Tutong". www.kheu.gov.bn (in Malay). Retrieved 30 August 2017.
- ^ "3 Things to Do while Transiting Through Tutong". Brunei Tourism. Retrieved 14 June 2022.
- ^ Kampong Ayer: warisan, cabaran, dan masa depan : kumpulan esai yang pernah diterbitkan 1970-1996. Akademi Pengajian Brunei, Universiti Brunei Darussalam, Negara Brunei Darussalam. 1996. p. 29.
- ^ Haji Julaini & Haji Idris 2012, p. 14.
- ^ "Kompleks Sukan Tutong". www.belia-sukan.gov.bn (in Malay).
Sources
[edit]- Haji Julaini, Sastra Sarini; Haji Idris, Hajah Noorhijrah, eds. (2012). Tutong District (PDF) (2nd ed.). English News Division, Information Department, Prime Minister's Office. ISBN 99917-49-34-9. Retrieved 4 September 2024.
- Chua, Thia-Eng; Chou, L. M.; Sadorra, Marie Sol M. (1987). The Coastal Environmental Profile of Brunei Darussalam: Resource Assessment and Management Issues. WorldFish. ISBN 978-971-10-2237-2.
- Department of Agriculture and Agrifood (2022). Agriculture & Agrifood Statistics in Brief 2022 (PDF). Ministry of Primary Resources and Tourism.
- Department of Fisheries (2021). Brunei Darussalam Fisheries Statistics (PDF). Ministry of Primary Resources and Tourism.
- Sidhu, Jatswan S. (22 December 2009). Historical Dictionary of Brunei Darussalam. Scarecrow Press. p. 217. ISBN 9780810870789.
- Page, Kogan (2003). Asia and Pacific Review 2003/04: The Economic and Business Report. Kogan Page Publishers. ISBN 978-0-7494-4063-3.
- Silvestre, Geronimo (1992). The Coastal Resources of Brunei Darussalam: Status, Utilization and Management. WorldFish. ISBN 978-971-8709-11-5.
- Cohen, Saul Bernard (2008). The Columbia Gazetteer of the World: P to Z. Columbia University Press. ISBN 9780231145541.
- Pusat Sejarah Brunei (2002). Puak Tutong: sejarah dan perkembangan awal sosio-budaya (in Malay).
External links
[edit]- (in Malay) Tutong District Office website






